



![]()
![]()

Strike Fighter Squadron FOURTEEN [VFA-14]
VFA-14, Tophatters, is based at NAS Lemoore in California. They were redesignated VFA-14, from VF-14, in 2001. This was to reflect VFA-14's transition training to the F-18E/F Super Hornet.
The Tophatters had previously been flying the F-14 Tomcat.
At the beginning of 1999, the Tophatters of VF-14 celebrated their 80th year of continuous active service. Being the US Navy's oldest continuous active duty squadron, Tophatter history is very much a history of naval aviation. The squadron was established in September of 1919 at NAS San Diego, and since its inception has had fourteen different squadron designations and flown over twenty-two different types of aircraft. Fighter Squadron Fourteen has operated from no less than twenty two kinds of cruisers, battleships, and aircraft carriers, carrying the United States flag to all corners of the seven seas.
The squadron's career began on the US Navy's first carrier, USS Langley, (CV 1). The squadron, then Fighter Plane Squadron 1, established a record for carrier landings in a single day. Flying the TS-1 aircraft, one hundred twenty seven landings were completed by the end of flight operations.
As for the top hat, it was originally adopted in 1927. Devised by then commanding officer, LCDR Gerry Bogan, the unit emblem was meant to symbolize the very best, and to boost the morale of the aviators who were flying the notoriously difficult Boeing FB-5. Originally called the High-Hatters, the title changed in 1942 to the more modern ~~Top hat" moniker.
Over the years, the squadron has been assigned many different missions, including patrol and observation in its early years, and scouting, attack, and fighter when it became associated with carrier based operations. In 1929, the squadron was assigned to USS Saratoga (CV 3), where it began as a fighter squadron and transitioned to a bomber squadron. Throughout the 1930's the Tophatters flew various aircraft before being transferred to the Atlantic fleet and USS Ranger (CV 4).
The Tophatters proved formidable foes during World War II. The squadron saw action in North Africa and against German forces in Norway. In November of 1944, the squadron transferred to the Pacific Fleet and participated in various campaigns. In 1949, while flying the F-4U Corsair, the Tophatters accepted their current designation as VF-14 as well as the role of all weather interceptor.
In 1954, they transitioned to the jet age with the F3-D Skynight and shortly thereafter, in 1956, to the F-3H Demon. In May 1963, the Tophatters transitioned to the F-4B Phantom II and on 23 January 1963 they became the first Phantom squadron to operate onboard the USS Franklin D. Roosevelt (CVA 42). In January 1974 the squadron transitioned to the F-14A Tomcat and in June 1975, the Tophatters became the first squadron to deploy to the Mediterranean with the F-14A Tomcat.
What followed was a very successful period for Fighter Squadron Fourteen, employing the Tomcat in various conflicts throughout the world including over 80 combat missions while engaged in operation "Urgent Fury" over Grenada. Shortly after that they were participating in operations off the coast of Lebanon in support of elements of the multinational forces in Beirut.
They were on extended deployment during the Lebanon Hostage crisis of 1986 and were on station with the USS John F. Kennedy (CV 67) shortly after the 1990 invasion of Kuwait by Iraqi ground forces. In January 1991, the Tophatters again saw combat during operation Desert Shield and Desert Storm.
Dark times fell on the squadron when in April 1994 they were transferred to Commander, Fighter Wing Atlantic in anticipation of decommissioning. Two aviators were recovered following their ejection from an F-14 Tomcat that crashed into the Atlantic Ocean, approximately 75 miles off the coast of Virginia at 11:50 a.m. 23 March 1995. The aviators of Fighter Squadron (VF) 14, based at Naval Air Station Oceana, were on a routine training flight.
The squadron was given a reprieve and began building up again in 1996 in anticipation for a 1997 summer Mediterranean cruise onboard the USS John F. Kennedy (CV 67).
Following a very successful deployment, the squadron spent most of 1998 at home in Virginia Beach while looking forward to their 80th anniversary deployment onboard the USS Theodore Roosevelt (CVN-71). The Tophatters spent fifteen months preparing for this deployment period. They practiced their gunnery and Air Combat Maneuvering skills in Key West in February 1998; fought against F-15s and F-16s while working with the Air Force in Panama City, Florida in March 1998; then they started the initial phases of the work-up cycle beginning with Air-to-Air Strike-Fighter Advanced Readiness Program (SFARP) in Oceana in June 1998. That was followed shortly by Air-to-Ground SFARP in El Centro, California.
Finally, their first embarkation on the Roosevelt came in early September 1998 for the initial phases of the carrier work-up cycle. Then it was off to Fallon, Nevada in October 1998 for several weeks of Airwing training; followed by a six week embarked period on the ROOSEVELT to practice what was learned in Fallon. One final embarked training period came in
February 1999 before Airwing Eight and the Roosevelt team was considered "ready for deployment."
The Tophatters brought the latest technology with them on this deployment, as the F-14A Tomcat had seen numerous modifications in the previous year. The latest change was new software for the Tomcat's AWG-9 radar control system. Designed in the 1960's and one of the oldest air-to-air radar systems, the AWG-9 is still the most powerful and the new software will increase its capabilities for the 21st century. One of the improvements was the incorporation of a new Digital Flight Control System (DFCS) that replaced the analog system in use since the aircraft's inception.
All pilots agree that the Tomcat is now more maneuverable and has crisp response to pilot control inputs. Along with the DFCS modification came a new, more advanced Radar Warning Receiver that gives the Tophatter aircrew earlier and more accurate indications of enemy radar trying to detect and lock onto their aircraft. Another significant improvement was an upgraded software package for the LANTIRN pod, the infrared targeting and tracking pod which allows the Tomcat to employ numerous types of laser guided munitions.
The enhanced software allows the F-14 to more accurately employ weapons as well as record more accurate target coordinates. Using the newly installed Fast Tactical Imagery (FTI) system, the F-14A Aircrew can transmit digital images captured from the LANTIRN pod video to another Tomcat or to the Battle Group Commander. These images could be used for immediate attack by another aircraft, for damage assessment, for locating targets of opportunity, or simply for determining precise coordinates for targeting by other weapons.
When ROOSEVELT and VF-14 departed Norfolk, Va. For a routine six-month deployment on March 26, 1999, they were slated to relieve USS Enterprise Battle Group in the Arabian gulf. However, after a high-speed Atlantic transit, the T.R. was diverted to the Ionian Sea on April 6 to support Operation Allied Force, the NATO-lead air campaign in Kosovo. It would be the first time in NATO’s history that the organization collectively authorized military action. On 14 July 1999, T.R. and VF-14 arrived in the Arabian Gulf.
They relieved USS Kitty Hawk of Operation Southern Watch duties of enforcing the No-Fly Zone in Southern Iraq. Four days later, on July 18, CVW-8 F/A-18's and F-14's conducted their first strike in theater with precision guided munitions against an Iraqi surface-to-air missile site approximately 200 miles south of Baghdad, and an Iraqi military communications site 150 miles southeast of Baghdad.
The squadron returned home to NAS Oceana to proudly celebrate 80 years of continuous active duty, now more than ever the "oldest and boldest" Fighter Squadron in the Navy. Recently, Carrier Air Wing Eight and VF-14 changed their home to the nuclear powered aircraft carrier USS Enterprise (CVN-65).
In Spring 2001, VF-14 deployed with CVW-8 on board the CVN-65 Enterprise. Following the terrorist attacks of Sept. 11, 2001 VF-14 participated in the air strikes against Afghanistan. After returning to Norfolk in mid-November 2001 VF-14 began to transition to NAS Lemoore where its designation changed to VFA-14 and it received Super Hornets.
Among the many awards held by the TOPHATTERs are two Presidential Unit Citations, the Navy Unit Commendation, two Meritorious Unit Commendations, five Battle stars, four CNO Aviation Safety awards, and eight COMNAVAIRLANT Battle Efficiency "E" awards - the last one for 1999!.
They were also presented the most coveted trophy of excellence in the fighter community - the Admiral Joseph C. Clifton award - at the Association of Naval Aviation (ANA) convention in May 1998. This award was soon followed by an equally prestigious and exceptional honor - the Arleigh Burke Fleet Trophy, awarded annually to the most improved combat unit (ship, submarine, or squadron) in Commander in Chief, U. S. Atlantic Fleet (CINCLANTFLT). This award has never before been won by an F-14 squadron, and it is perhaps this last award which says the most about where Fighting Fourteen has been and where it is going as the squadron sails into the third millennium.
With the squadron successfully transitioned the pace picks up considerably as VFA-14 prepare for work-ups and a deployment on the USS Nimitz (CVN-68).
Their adventure started near the middle of 2002 with an air-to-air training detachment in Portland, OR. Followed by the Strike Fighter Air Combat Readiness Program (SFARP) in Fallon, NV. The end of 2002 had the mighty TOPHATTERSs returning to Fallon to complete their Air Wing Training during the month of December. Finally during the months of February and March of 2003, VFA-14 concludes work-ups with JTFX combined with COMPTUEX off the coast of San Diego aboard the Nimitz.
After a very short period of leave VFA-14 quickly return to the USS Nimitz (CVN-68) and steam West bound to the Persian Gulf. Today you can find the TOPHATTERs comfortable aboard the Nimitz conducting various flight ops. As the war with Iraq comes to an end VFA-14 have and continue flying many combat sorties to show US presence in Iraq and support for Coalition ground forces.
![]()




![]()
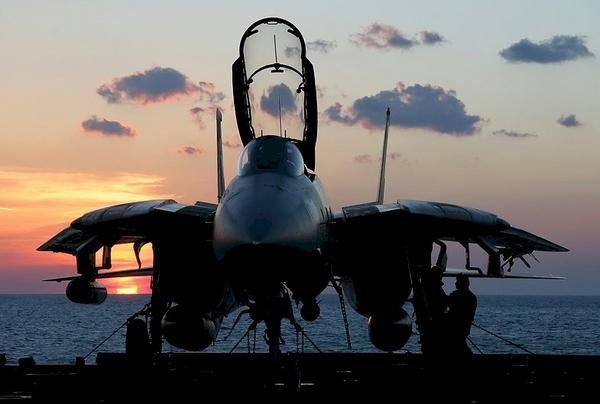
F-14 TOMCAT
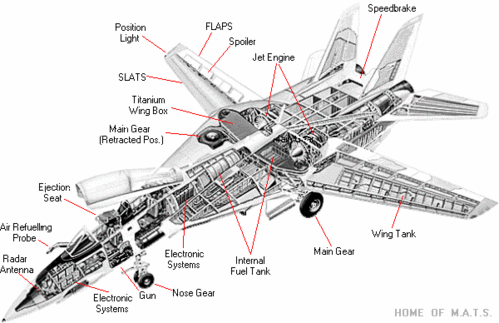
The F-14 Tomcat is the US Navy's carrier-based two-seat air defence, intercept, strike and reconnaissance aircraft. The aircraft was developed by Northrop Grumman to replace the F-4 Phantom fighter and entered service with the US Navy in 1972. In 1987, the F-14B with an upgraded engine went into production. Further upgrades in the radar, avionics and missile capability resulted in the F-14D Super Tomcat, which first flew in 1988.
The US Navy operated 338 F-14 aircraft of all three variants, but the aircraft is being replaced by the F/A-18E/F Super Hornet. In July 2006, the F-14 made its last carrier launch and, on September 22nd 2006 the US Navy officially retired the F-14 Tomcat.
The variable sweep wing and the twin almost upright tail fins of the F-14 Tomcat give the aircraft its distinctive appearance. The variable sweep wings are set at 20° for take-off, loitering and landing, and automatically change to a maximum sweep of 68°, which reduces drag for high subsonic to supersonic speeds. The wings are swept at 75° for aircraft carrier stowage.
COCKPIT
Catseye night-vision goggles have been installed in the F-14 since 1996 and are supplied by BAE SYSTEMS. The F-14D front cockpit is equipped with a head-up display and two multifunction flat-screen displays. The rear cockpit for the Radar Intercept Officer is equipped with a display that presents fused data from the AN/APG-71 radar and from the suite of aircraft sensors.
82 US Navy F-14Bs are being upgraded with Flight Visions, Inc. Sparrow Hawk HUD and FV-3000 modular mission display system, which will improve reliability and night-vision capability. The cockpit is equipped with the NACES zero/zero ejection seat supplied by Martin Baker Aircraft Company.
WEAPONS
The F-14 is armed with a General Electric Vulcan M61A-1 20mm gun with 675 rounds of ammunition, which is mounted internally in the forward section of the fuselage on the port side. The aircraft has eight hardpoints for carrying ordnance: four on the fuselage and two each side under the fixed section of the wings.
The aircraft can carry the short-, medium- and long-range air-to-air missiles AIM-9, AIM-7 and AIM-54, and air-to-ground ordnance including the Rockeye bomb and CBU cluster bombs. Raytheon AIM-7 Sparrow is a medium-range radar-guided air-to-air missile with range of 45km.
Lockheed Martin/Raytheon AIM-9 Sidewinder is a short-range air-to-air missile with a range of 8km. Raytheon AIM-54 Phoenix is a long-range air-to-air missile with a range of 150km. The F-14 can carry up to six Phoenix missiles and is capable of firing the missiles almost simultaneously at six different targets. The Phoenix missile was retired from US Navy service in October 2004.
The F-14D can carry four Joint Direct Attack Munitions (JDAM). First operational deployment of a precision-guided JDAM from an F-14 was in March 2003.
In 1995, the US Navy installed the Lockheed Martin LANTIRN precision strike navigation and targeting pod on the F-14.
The LANTIRN targeting pod includes a dual-field-of-view FLIR and a laser designator/rangefinder. The navigation pod also contains a FLIR and terrain-following radar. A Lockheed Martin infrared search and track system is installed in a sensor pod under the nose.
SENSORS
The F-14D is equipped with a Raytheon AN/APG-71 digital multi-mode radar, which provides non-cooperative target identification, and incorporates low sidelobe techniques and enhanced frequency agility.
The F-14 carries a tactical air reconnaissance pod system (TARPS), which carries a Recon/Optical KS-87B forward or vertical frame camera, and a low-altitude panoramic view KA-99 camera, together with a Lockheed Martin AN/AAD-5 infrared linescanner.
The pod is equipped with a digital imaging system for the transmission of near real-time imagery to the aircraft carrier command centre via a secure UHF radio data link. To supplement TARPS, US Navy F-14s are also being fitted with a fast tactical imagery (FTI) system, which is a line-of-sight system for targeting and reconnaissance.
COUNTERMEASURES
The aircraft is equipped with the BAE Systems Integrated Defense Solutions (formerly Tracor) and Lockheed Martin AN/ALE-39 and AN/ALE-29 chaff, flare and decoy dispensers. The Super Tomcat has a Raytheon AN/ALR-67(V)4 radar warning system and BAE Systems Information & Electronic Warfare Systems (IEWS) (formerly Sanders) AN/ALQ-126 jammer.
ENGINE
The F-14B and the F-14D have two General Electric F110-GE-400 turbofan engines, rated at 72kN and 120kN with afterburn. There are five internal fuel tanks, which carry 9,000 litres and are located in the fixed section and the outer section of the wings, and in the rear section of the fuselage between the engines.
![]()



CVN 67 John F. KENNEDY
The USS JOHN F. KENNEDY was the last conventionally-powered aircraft carrier built by the US Navy.
Originally scheduled to become the fourth KITTY HAWK class carrier, the JFK received so many modifications during construction that she formed her own class. Named in honor of the 35th president of the United States, John F. Kennedy who was assassinated on November 22, 1963 in Dallas, TX., the USS JOHN F. KENNEDY was the first ship in the Navy to bear the name.
Transfered to the Naval Reserve Force in 1995, the KENNEDY returned to the active fleet again in October 2000. The Navy initially wanted to decommission the KENNEDY in mid-2005 because the carrier was in bad shape and was in need of expensive repairs that just did not seem to be cost-effective. However, the Congress decided to keep the KENNEDY in service to have a total of 12 active aircraft carriers.
The JOHN F. KENNEDY was subsequently berthed at the Mayport Naval Station for several months. Her flight deck was not certified for aircraft operations and the Navy was just waiting to finally decommission the ship. In late 2006, the decision was finally made to retire the KENNEDY. The KENNEDY made a final voyage up the east coast for a final port visit to Boston, Mass., in early March 2007.
The decommissioning ceremony for the JOHN F. KENNEDY was on March 23, 2007, at Mayport, Fla.
The official decommissioning date for the USS JOHN F. KENNEDY was August 1, 2007.
Nimitz class aircraft carrier

Tomcat Glory
Super Funny F-14 Video!!!
F-14s shooting down Libyan Mig-23






















/idata%2F0396584%2FKOREA%2F71910_korea_MIA1_800.JPG)
/idata%2F0396584%2FU.S.ARMY-POST-WW2%2Fphot4901a.jpg)
/idata%2F0396584%2FDRAWINGS-UNIFORMS-WW2%2F30-451-09b-2.jpg)
/idata%2F0396584%2FP-40%2F44FS000.jpg)
/idata%2F0396584%2FGERMAN-U-BOAT%2FBundesarchiv_Bild_101II-MW-1031-28-_Lorient-_U-31.jpg)
/idata%2F0396584%2FSOVIET-ARMY-WW2%2F1.jpg)




